General overview with examples
by Dr. Arno Smit Orthopaedic Surgeon White Rock, BC
Please Note: The information contained in this presentation was most accurate in 2004. Orthopaedic technology and practice changes over time. Always consult your doctor to ensure the information applies to your case.
- Role of Surgery in Arthritis Treatment
- Pain Relief Only
- Ankle
- Pre-Op
- 1 Year Post Fusion
- Prosthetic Replacement
- Current Trends
- Shoulder Replacement
- X-ray: Before Surgery, RA
- X-ray: Rotator Cuff Deficient - Stem, RA
- X-ray: Rotator Cuff Deficient - Copeland, RA
- X-ray: Rotator Cuff Intact - Copeland, Osteo-Arthritis
- Hip Replacement
- Stemmed Hip Replacement
- Bearing Surfaces - Wear Rates
- Implants
- Bone Preserving Hip Replacement
- X-ray: Before Surgery- Osteo-arthritic Hip
- X-ray: Birmingham Hip
- X-ray: Birmingham Hip
- Why or why not Bone Preserving?
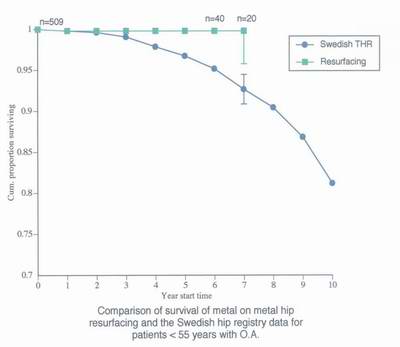
- Comparison of Survival
- Technology & History
- Conclusions
- Knee Replacement Surgery
- Implants
- Total Knee Replacement
- Partial Knee Replacement (Unicompartmental Knee Replacement
- Types of Partial Knee Replacment
- Prerequisites for surgery
- X-ray: Standing
- X-ray: Stress Views
- X-ray: Partial Knee Replacement
- X-ray: Partial Knee Replacement
- X-ray: Partial Knee Replacement
- X-ray: Partial Knee Replacement
- Conclusion
- Thank You!
Role of surgery in arthritis:
Prevention: create normal joint surface
- after trauma
- for certain developmental joint abnormalities
Modulation: slow down the progression
Restoration:
- biological
- prosthetic replacement
Pain relief only:
Surgery for pain relief only
Excise painful joint
- Usually poor control of joint motion (flail)
Eliminate pain through elimination of motion
- Fusion surgery
- Commonly used in smaller joints
- Now rarely used in large joints
- Main option in spine, ankle, foot, wrist, hand
End-stage Osteo-Arthritis ankle, pre-op
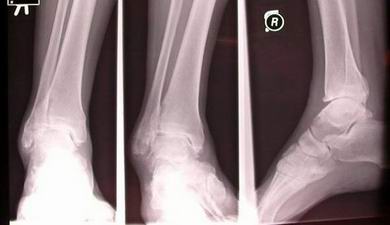
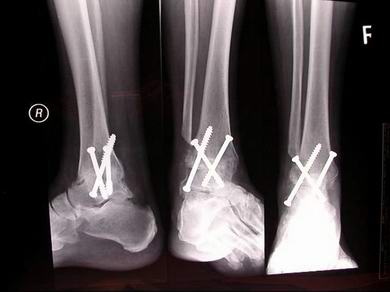
End-stage O.A. ankle, 1 year post ankle fusion
Prosthetic Replacment Surgery
- Eliminate arthritic pain by providing smooth gliding joint surface.
- Optimize range of motion and functional capacity
Prosthetic replacement surgery
Current trends:
- implants more 'bone-and-joint' friendly
- better bearing surfaces
- less-invasive surgery
- 'recover faster and better'
Shoulder replacement
Ball and 'shallow socket' joint
- 'Socket' replacement controversial
- 'Ball' replacement well established
- Traditional stemmed design
- More recent: bone-preserving design
Shoulder replacement, Rheumatoid Arthritis Before Surgery
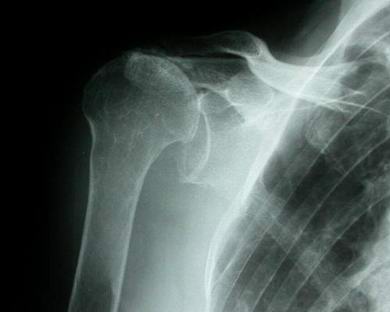
Shoulder Replacement, Rheumatoid Arthritis
rotator cuff deficient, stem
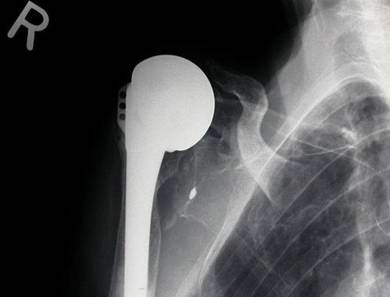
Shoulder Replacement Rheumatoid Arthritis
rotator cuff deficient, Copeland
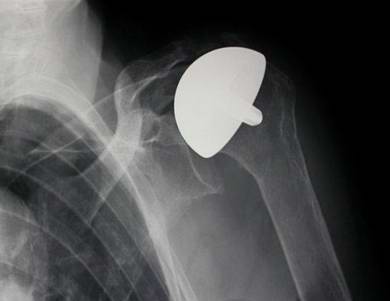
Shoulder Replacement Osteo-Arthritis
rotator cuff intact, Copeland
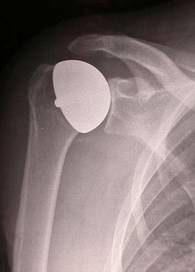
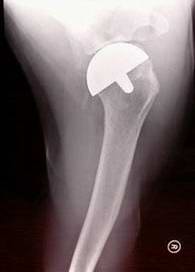
Hip replacement
Ball and 'deep socket'
Both are replaced
- Traditional stemmed design
- More recent bone-preserving design
Stemmed hip replacement
Well-proven technology
Recent improvements:
- better bearings
- less-invasive surgery
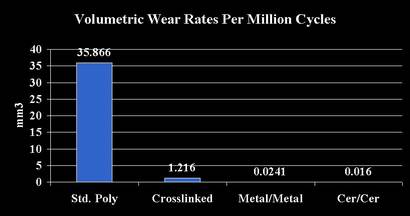
Hip replacement -bearing surfaces
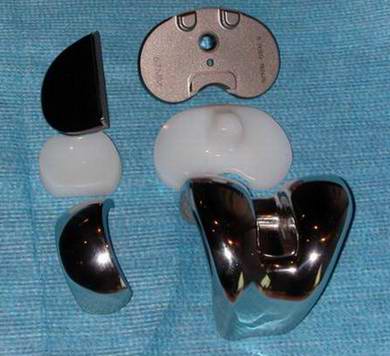
Hip replacement: implants

Hip replacement: bone preserving
For the 'young and vigorous'
Resurfacing of femoral head
Metal-on-metal bearing
Allows higher activity level
Requires full traditional exposure
Unknown: possibility of toxicity of metal in long run
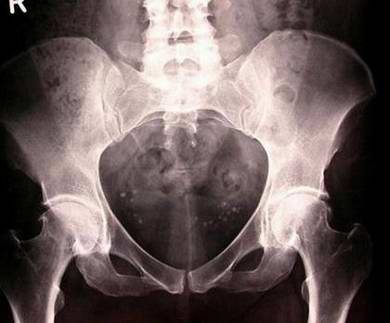
Osteo-arthritis left hip, 52 y old woman
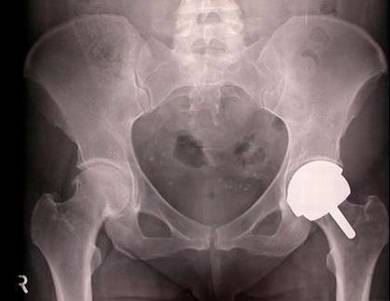
Osteo-arthritis left hip Birmingham hip
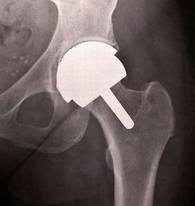
Osteo-arthrosis left hip Birmingham hip
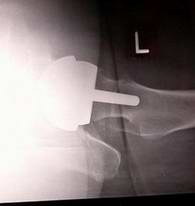
Hip replacement: bone preserving
Why?
Will last longer
More options for revision after failure
But: upfront costs are higher-->
difficulty with funding
Hip replacement: bone preserving
Cobalt Chrome Alloys
Hip replacement
So:
1/ older and more sedentary-->
refine standard hip replacement
2/ younger and more vigorous-->
refine standard hip replacement
OR
consider metal-on-metal resurfacing
Knee replacement
Total knee replacement:
- well established
- big operation
Newer trend:
- if possible, consider less invasive partial knee replacement
Knee replacement: implants
Knee replacement: total
If entire knee 'worn out'-->
Total knee replacement is by far the best solution
Knee replacement: partial
If only part of the knee 'worn out'-->
Partial knee replacement.
Less invasive
Faster and better recovery
'Don't burn bridges'
Knee replacement: partial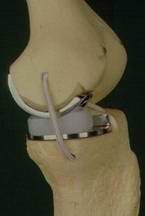
vs.
Knee replacement: partial
Step 1: Must demonstrate intact opposite compartment
Step 2: Must demonstrate ACL integrity for mobile bearing knee
Knee replacement: partial, Standing
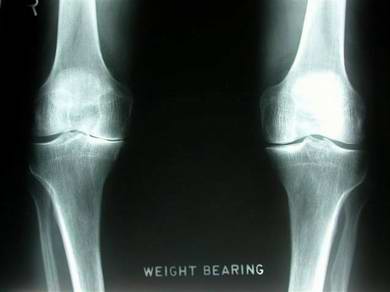
Knee replacement: partial, Stress views
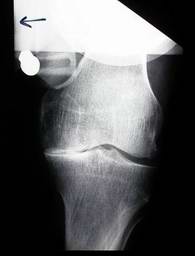
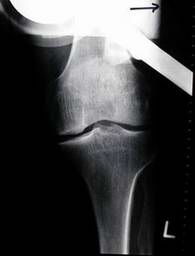
Knee replacement: partial
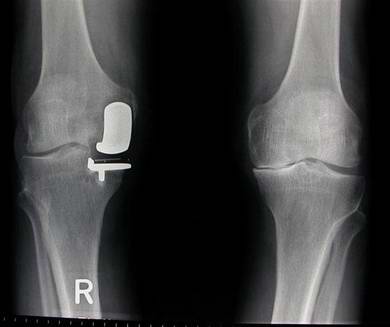
Knee replacement: partial
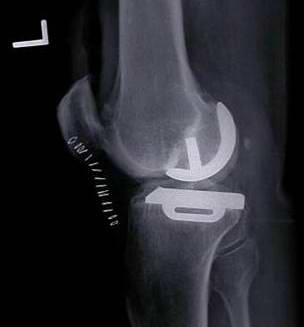
Knee replacement: partial
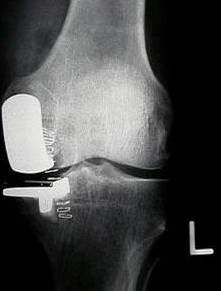
Knee replacement: partial
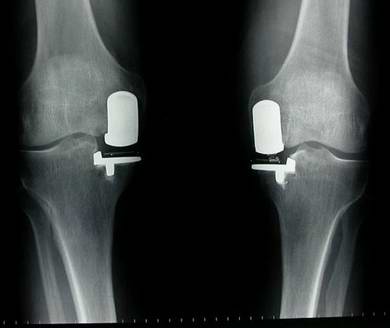
Conclusion
- Surgery will remain an important tool to deal with end-stage, disabling arthritis
- Improvements in materials, design and surgical technique continue to be refined
- Biological solutions for end-stage arthritis are NOT imminent
- The main issue today is ACCESS.
Thank You !!!
